Odisha State Board CHSE Odisha Class 11 Psychology Solutions Unit 3 Learning Long Answer Questions Part 2.
CHSE Odisha 11th Class Psychology Unit 3 Learning Long Answer Questions Part-2
Long Type Questions with Answers
Question 1.
Discuss the meaning and operational definition of learning?
Answer:
Meaning and operational definition of learning:
Learning has been described by some as a modification of behavior. In learning vocabulary, tennis, football, remembering a poem, learning typing, or driving modification of behavior takes place. As a result of repeated practice modification of behavior takes place whether it is sensory, motor or psychological learning starts with an absolute zero. But this definition is too wide and suffers from vagueness. All modifications of behavior cannot be called learning. Some cases of change of behavior appear like learning from the surface. Once not actually learning modification of behavior due to:
- Sensory adaptation
- Maturation
- Fatigue
- Drugs cannot be attributed to learning
Sensory adaption:
When you entered the class you got the strong smell of perfume. But after a few minutes, you are no more aware of the fragrance as the Olfactory sense organ has adapted very quickly. This insensitiveness to the smell of perfume is not because of previous learning but because of the adaptability of the Olfactory senses of the individual.
Maturation:
Two kinds of changes in behavior take place: Those changes which occur due to endogenous (internal) factors are called changes due to growth and maturation, Those changes in behavior that take place due to external factors like environment are called learning changes, called maturational changes. Thus, due to maturation birds start signing at a particular period. The human babysits, stands, walks, and babbles at a particular age. Sexual growth starts at a particular age and so on.
Changes in behavior due to maturation should not, therefore, be confused with changes in behavior due to learning. Changes due to maturation are usually stereotyped and practically identical to all members of the species. But most of the learning changes are varied, also behavior changes due to abnormal glandular secretion, brain damage, and disease should not be attributed to learning.
Fatigue:
A decrement in work performance takes place because of fatigue or tiredness. Fatigue decreases efficiency. A student who is taking down notes in the class at a fantastic speed in the early hours, may not be able to write at the same speed in the last hours. comparative change in performance is not due to learning, but due to fatigue. A person is instructed to draw two parallel lines as quickly as possible for an unlimited period.
After some time, the performance gradually decreases and a period comes when he cannot move his wrist any further. Does this work decrement take place because of practice, due to learning? No, it is not due to practice or learning. It is due to fatigue. This work decrement is also temporary and disappears after rest or change in work.
Drug:
After taking some drugs, some people may suffer from the “drug effects”. The effect of drugs brings a complete change in their behavior for a temporary period. This change in behavior of the ‘ O ’ is not due to practice and hence cannot be attributed to learning. Further temporary that it cannot be called a case of learning.
In view of these facts, learning can be described as a permanent modification of behavior as a result of past experience and practice. Practice reinforces learning firstly, the change in behavior must be more or less, permanent and secondly, it must be the effect of past experience and practice. Any modification of behavior not due to past experience and practice cannot be attributed to learning.
Learning can also be defined as a progressive improvement in performance as a function of practice. No improvement in performance would be possible if the practice does not result in cumulative retention. Secondly, the change that we refer to in learning must be a quantitative and measurable change in performance. The following table demonstrates the measurable change in the performance of a person while learning typing.
| Day | Errors | Av. Performance in 30 Minutes |
| 1 | 25 | 15Owords |
| 2 | 32 | 180 words |
| 3 | 34 | 190 words |
| 4 | 30 | 190 words |
| 5 | 25 | 200 words |
| 6 | 15 | 230 words |
| 7 | 15 | 230words |
| 8 | 12 | 250words |
| 9 | 06 | 300 words |
| 10 | 00 | 320 words |
Both reductions in error and an increase in the speed of typing day by day suggest that the output of learning can be measured by trial. A number of different learning psychologists have emphasized different aspects of learning in their definitions. Some of them are discussed below Boaz (1984) defines learning as the process by which the individual acquires various habits, knowledge, and attitudes that are necessary to meet the demands of life in general.
Learning according to Boaz is a continuous psychological activity that takes place to solve the problems, needs, and demands of the concerned person. Secondly, by learning he develops those attitudes, knowledge, and habits that are required to meet the specific needs of problems of the learner. A person leams typing and shorthand to get a paying job as a personal secretary. A student leams cycling, so as to cover the distance from his residence to school.
A housewife leams the operation of electrical gadgets for the smooth functioning of domestic work, a girl learns cooking, knitting, and signing to have better prospects in the marriage market. Thus, Boaz emphasizes the motivation behind every learning. Learning by Morgan and King (1978) is defined “as any relatively permanent change in behavior which occurs as a result of practice and experience.” thus he deals with three major elements Learning is a change in behavior.
it is a change that takes place through practice and experience. Before it can be called learning, the change must be relatively permanent; it must last a fairly long time. According to Garrett, “Learning is that activity by virtue of which we organize our response with new habits.” Thus the element of organization in learning cannot be overlooked according to Garrett. In the opinion of Woodworth, learning a new thing adds to one’s experiences. He emphasizes the role of reinforcement in learning by saying it is indispensable for learning.
Woodworth and Scholasberg have given a very comprehensive definition of learning. According to them, “Learning is a change that occurs in the ‘O ’during any kind of activity. It shows later on after the effect of activity. A later activity is different from the earlier activity. We are tempted to say that learning is demonstrated when even a later activity shows some after-effects of earlier activity.
According to Ruch (1970), Learning is a process that brings about changes in the individual s way of responding as a result of contact with aspects of the environment. Ruch views that behavioral changes induced by drugs, brain injury, and maturation are not considered to involve learning Hilgard has defined.
learning as follows Learning is the process by which an activity originates or is changed through training procedures as is distinguished from changes by factors attributable to training. According McGcoch, “Learning as we measure it is a change in performance as a function of practice. In most cases, if not in all, this change has a direction which satisfies the current motivating conditions of the individual.”
![]()
Question 2.
What is trial and error of learning? Describe the process of trial and error learning with an experiment?
Answer:
Methods or process of Learning :
How learning takes place? This has been a major issue for many decades and various methods have been developed for learning psychologists to explain how learning takes place. Theories of learning explain the learning process. Mainly the learning theories can be classified into two groups on the basis of their approaches. Stimulus – Response Theory supported by Thorndike, Pavlov, Skinner, Hull, Guthrie, etc. Cognitive Theory is supported by Kohler, Koffka Tolman, Lewin, etc.
The S-R theorists argue that learning occurs by habit due to a chain of reflexes. The ‘ O ’ learns to perform an activity by repeating the performance which brings the correct response or which leads one to reach the goal. This sort of learning process according to them takes place purely mechanically due to habit, due to stimulus-response association.
It does not require the understanding, the brain, or the intelligence of the learner. Paradoxically, cognitive theorists stress the role of organism variables in any learning. They argue that for any learning process to continue, intelligence, understanding, cognitive structure, etc. play an important role. Thus, they stress the role of brain processes in learning. They emphasize the means and the end, and understanding of the situation as a whole.
E.L. Thorndike’S Contribution To Trial And Error Learning:
The psychology of learning owes its existence to American Psychologist E.L. Thorndike (1874¬1949) for his first scientific study of learning. A glance at the contemporary situation of learning psychology indicates that for over half a century, the whole scene of learning psychology has been dominated by one person directly or indirectly and he is E.L. Thorndike.
It is also interesting to note that Thorndike has many followers as well as haters and rivals. When he first propounded his theory of Trial and Error Learning, it produced quite a stir in psychology. Tolman has, therefore, rightly pointed out, “He may be a starting point of attack.”. So, it is said that the psychology of animal learning, not to speak that of child learning, has been or still is primarily a matter of agreeing or disagreeing with Thorndike or tiyin in minor ways to improve upon him.
Prior to Thorndike, nobody did deal with the problem of motivation, not even Wundt or Ebbinghaus. But Thorndike brought a radical change in the history of psychology by bringing motivation into the picture. He conducted a large number of experiments on animal learning, and contemporary psychology and came to the conclusion that animals have no rational faculty in learning. They do not leam by reasoning but by trial and error.
Trial And Error Learning:
Animals go on hitting the target by impulse or leam out of a blunder of hit and miss. This is called Trial and Error Learning. Among the random hits, the correct response which is rewarded is ‘ Stamped in’. The wrong response which is not rewarded is ‘ Stamped out’. Thus; stamping incorrect responses and stamping out wrong ones is the core of learning according to Thorndike.
Trial and error is the simplest form of learning. It came into existence by means of animal experimentation. The trial and error method means trying one way to escape, reach the food or solve a problem, becoming unsuccessful and so trying another way. In this manner, the animal tries and tries until the correct solution is achieved until the goal is reached. The correct response is then repeated to strengthen the S-R connection.
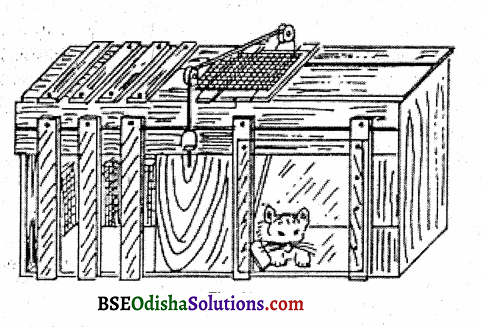
This sort of hit-and-miss learning proceeds slowly, and gradually. The errors fall slowly. The process of selecting and rejecting consists of this gradualness. On the basis of his vast amount of findings on animal experimentation. Thorndike viewed that animals come to leam things quite by chance rather than by anything like understanding. They learn blindly, mechanically, and randomly.
The solution comes by chance, accidentally. To study animal learning by Trial and Error method. Thorndike conducted a classic experiment on a hungry cat, which is described below A hungry cat was put inside a puzzle box. A piece of food (motivation) was kept outside the box at a little distance so that the cat cannot reach it unless she opens the door of the puzzle box. The cat had to press the lever by pulling the loop of the chord to open the door and to get the fish.
At first, the cat tried a number of ways and made lots of unnecessary movements to open the door. The random movements included clawing, biting, pulling, pushing, thrusting, and paws through any opening and the like. In this way after trying several hit-and-miss random acts, making enough struggle, accidentally, the loop was pulled and the door opened.
Finally, the animal reached its goal. Time taken for reaching the food was recorded. After several trials like this, the cat learned to go straight to the lever, press it, open the door and reach the food. A comparison of the time and unnecessary movements from the first to the last trial showed a gradual decrement in the time taken to reach the food.
Also, the unnecessary movements gradually decreased. This type of random hit-or-miss, exploratory activity is called Trial and Error. When these data are plotted into a curve, the irregular slopes at places indicate that animals do things accidentally without understanding. In this case, the cat leams through errors.
Question 3.
Discuss the stages of trial and error learning?
Answer:
Stages of Trial and Error Learning:
Need or Drive:
For any learning to operate need or drive is essential. It goals or motivates the organism to action. In Thorndike’s experiment, the cat was hungry. Hunger was the drive and the need was to get food. In certain cases when the cat is not hungry, the drive for exploration may serve as the need in learning the maze. The motivation should be goal oriented.
For instance, the cat is hungry. But there is no food outside the puzzle box. In this case, the animal will not try at all to open the door, unless, of course, the need to escape from the box operates as a goal. There must be some goal whatsoever, otherwise learning will not be effective.
Block or Resistance:
By preventing the direct release of tension blocks are created so that the animal would make attempts to learn. Without blocks, there cannot be any learning. Thorndike made many T & Y mazes and artificial blocks.
Random Movement:
Rigidity on the part of the ‘O’ does not help to learn quickly. Accidentally the rat heats so many paths; shows random, variable hit-and-miss kinds of activities that are blind, mechanical, and lack understanding and meaning.
Chance Success:
When the cat was trying to get the fish, it made many random unsuccessful activities. Out of these random attempts, by chance, accidentally, the ‘O’ succeeds in reaching the goal. So in .trial and error learning, success comes by chance.
Selection:
The successful movements or the correct responses which lead to the goal are reinforced and hence selected for further practice. The unsuccessful activities are discarded and the successful ones are encountered. This is called selection.
Repetition of the Successful Movements:
Repetition of successful movements leads to the establishment of a habit for a definite movement. When the cat found that certain selected movements led him to food, it attempted only those movements that enabled him to get out of the box and reach the food.
Fixation:
Fixation takes place due to habit, due to the repetition of the successful movements. The habit leads to a definite S-R connection. In fixation, certain essential factors like a decrease in time taken to reach the goal, no random movement, and anticipation of behavior observed. All the above principles are found generally, in any type of trial and Error learning.
![]()
Question 4.
Discuss briefly the curve of trial and error learning and maze learning?
Answer:
The curve of Trial and Error:
A curve can be drawn by taking the learning trial, a number of errors, etc. into consideration. The trial and error learning curve has the usual characteristics of a gradual decrease in time and error.
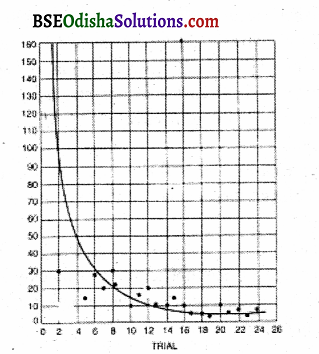
The blind and random activities, at last, come to an end. Errors become zero when the learning becomes perfect. But the time period never comes to zero because some time is necessary to reach the food object. It will vary from organism to organism according to its physiological limit A Japanese experimenter, Kuo did an experiment, on Maze. Shock chambers and confined chambers were allowed.
The shock was given in the earlier path but no food, he went in the short path but got shocked. So he went on another path but again got shocked. Finally, he went on another path and took more time to run. He learned the last path because it gave him reward and pleasure. In this case frequency with reward was found to be the effective answer. Kuo thus disapproved. Thorndike’s Frequency Theory by finding that frequency followed by motivation results in learning.
Kuo’s experiment concludes that practice always depends upon the consequence of reward. The rewarded learning is only fixated. Adam repeated Trial and Error Learning and formulated certain principles which opposed Thorndike’s. He conducted an experiment on discrimination learning where the monkey was trained to select a particular circle that brought him food.
There are two circles, one is big and the other is small. Food is always reinforced to the small circle. After some training, this big circle was substituted by a small circle which was smaller than the second one. In spite of this change in the size of the first circle, the monkey discriminated between the two circles and also learned to always respond to the circle which accompanied the food.
Here, Adam says, the monkey did not learn quite blindly but tried to perceive the relationship between the circles and discriminate one from the other. So he retorted, animals always do not learn by chance. Their activities are not always random or unsuccessful. Sometimes the animal tries to understand the situation and gives a response accordingly.
Thorndike counteracted this criticism by the argument that trial and error learning occurs in the case of lower animals only. Monkeys, chimpanzees, and human beings do not learn by trial and error. Adam conducted another experiment where even after 21 trials, the animal did not learn to open the latch because there was no reinforcement (food) outside the box. But when the smell of fish was noticed by the animal, it tried to open the latch.
Thus, Adam proved that motivation followed by practice strengthens learning. He proved that without motivation learning cannot be specific. This data also went against Throndike’s assumption and emphasized more practice for effective learning. The findings of several such studies led to severe criticism of the Law of Exercise of Thorndike. Thus after 1933 of Effect was included along with the Law of Exercise.
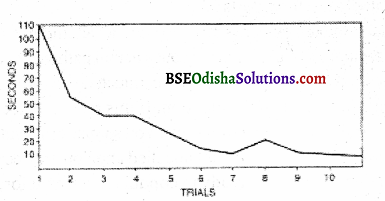
Maze Learning:
Several maze methods were used extensively to demonstrate trial-and-error learning. Maze refers to a number of complicated ways in which the ‘O’ tries to escape or to seek food. In such learning, time and errors are taken as criteria of learning. As the time and errors, reduce the ‘O’ is said to proceed toward learning. The number of unnecessary movements taken to reach the goal is counted as error. By making suitable readjustments, each time the ‘O’ attempts to improve his performance.
Question 5.
What is human learning define the meaning of the law of learning and explain different laws of learning?
Answer:
Human Learning:
Human beings also learn by trial and error method. A human ‘O’ is given to learning a complicated maze blindfolded. In the beginning, he makes several wrong movements though less in degree than, the animal. Gradually in a few trials, he learns the maze. Besides simple mazes, hand stylus and complicated mazes are also used in human learning. Trial and learning also take place in our everyday life.
Opening a lock by selecting from a bunch of keys without knowing the actual key, solving a sum by different formulas, sensory-motor learning like tracing star papers with the help of mirror drawing, typing, cycling, and other motor skills are all cases of trial and error learning. Though simple by nature, the trial and error method is said to be one of the most important methods of learning.
In some conditioning and insightful learning trial and error, the method is also involved. Trial and error learning can be overt and covert. Thinking is said to be covert or mental trial and error. However, the trial and error method does not take into account the importance of the whole situation in learning. It has always emphasized part learning, i.e., learning part by part.
Laws of Learning:
on the basis of several experimental findings on animal learning. Thorndike formulated certain laws to explain, the fundamental process of learning. Learning can be explained as an operation of these laws or principles. These laws explain the how and why of learning, a) Law, of Readiness It refers to the physical or psychological (mental) preparedness of a person to do a job or to attend to a stimulus.
If one is prepared to learn; or acquire something, he welcomes it and gets a satisfying feeling while doing it. Conversely, if one is not ready to receive a stimulus, he regrets it and demonstrates dissatisfaction while making a response. Thus, in the opinion of Thorndike, readiness for doing work makes learning smooth, pleasant, and economical.
The Law of readiness has three parts:
If there is, a conduction unit that is ready to conduct an impulse, the act of conducting is satisfying or pleasing. This unit is nothing but a neural pathway or a relay of neural. If there is a conduction unit that is ready to conduct, not doing so is annoying. You are all prepared to/run a race. You are in attendance. If this race is canceled suddenly you are annoyed.
You are all dressed for a film show. Your spouse or friend does not reach in time to accompany you to the show. So it is canceled and you are deeply annoyed. If there is a conduction unit not ready to conduct and if you force one to conduct that creates annoyance. For instance, when you are not ready to sing a song but are forced to do so, it creates annoyance.
Some critics of Thorndike argue that Thorndike in three formulations speaks entirely in terms of physiology, only neural readiness. But looking at these laws, it seems that no legitimate physiological meaning can be attached to them. Later students of Thorndike attempted to attach a more legitimate meaning to these principles.
They say that though Thorndike speaks in the language of physiology, he actually meant psychology. Thus they interpret the conduction unit as a readiness, a set, a preparedness for making a response tendency which is more a psychological readiness.
Law of Exercise:
It is the principle of repetition or the frequency principle. This law states that if an S-R connection is used repeatedly, the strength of that connection is increased and if an S-R connection is not used, the strength of that connection is weakened. Repetition, therefore, increases the strength of response and lack of repetition weakens it. Hence, the law of exercise is based on the principle “Practice makes one perfect. A person who has repeated a poem several times will remember it more than one who has not.
The Law of exercise comprises two short laws:
Law of use and law of disuse. The S-R connection is strengthened by using it and weakened by not using it. This law of exercise is defined in terms probability of response strengthening and weakening. This suggests that the response acquires proficiency when it is repeated. Proficiency decreases when it is not repeated.
Criticism – Other behaviorists Thorndike took the law of exercise as the sole principle of learning. They argued that it leads to the fixation of certain definite S-R responses, a tendency leading to specific learning. But many experiments including Adam proved that learning is net-specific as Thorndike thought. It is rather a general orientation. Adam and others found that the same animal used different methods to achieve the same goal.
Thus, considerable doubt is focused on the specific nature of learning. Secondly, subsequent learning psychologists did not find the law of exercise as effective as Thorndike thought. Mere repetition without motivation does hot achieves anything. The person must have some reinforcement or incentive to learn a skill. Otherwise, practice proves ineffective.
Several experiments on knowledge of results show that repetition without reinforcement does not bring learning. Japanese psychologist Kuo has also found the same thing. That learning becomes ineffective without an intention to learn is proven in most of our daily activities. In view of this criticism, Thorndike decided to Supplement the Law exercise with the law of effect.
Law of Effect:
It follows from the Law of Exercise. The Law of effect refers to Some kind of reward or reinforcement. It stresses the role of motivation in learning. It is the cornerstone, the cardinal principle of Thorndike’s theory of learning. Thorndike viewed that in all situations involving learning, be its sensory or motor or both, the principle of effect is exemplified. conditioning learning, insightful learning, and in trial and or learning, the law of effect is indispensable. This law is responsible for the selection of some goals and the rejection of others. The whole system of Thorndike, in fact, falls or rises with this law.
![]()
Question 6.
What is learning of performance and discuss the maturation of learning?
Answer:
Learning and Performance:
Sometimes learning is confused performance. But learning is different from performance. Learning cannot be directly observed, but it is inferred from performance. So learning contributes to performance, but it is only one ingredient of performance. Performance is affected by many factors other than learning. Performance refers to observed behavior while learning can only be observed through performance.
The several factors which influence performance are – need, motivation, attitude, past experience, and learning. Thus, among several factors influencing performance, learning is only one factor.
Learning and Maturation:
Learning basically depends upon the psychological system, i.e. the sensory organs and the cerebral cortex. The growth of organs, therefore, helps in learning. Whatever training we may give to a baby of 5 months, he cannot walk or speak a language. Similarly, a five-year-old boy cannot solve complex mathematical problems, because the solution to mathematical problems depends upon the development of intelligence and the cerebral cortex.
If the brain is not ready enough to grasp a thing, learning will not be possible. Thus it seems apparent that maturation of that organ is necessary, which is to be used for particular learning. What is Maturation? If simply refers to growth, both physically arid and mental. Munn (1954) opines that maturation in man depends upon the existence of human genes and human intracellular, intercellular, and external preconditions.
Those changes which take place due to endogenous or internal factors are called changes due to the influence of growth and maturation. Changes due to the influence of external factors are due to learning. Maturation mostly depends upon prenatal conditions and genes and partly upon the environment. Maturation can be accelerated or retarded by the postnatal environment because feedback from the early environment has also something to do with growth and maturation.
Maturation occurs after birth as well as before. Maturation greatly depends upon heredity. But since the early environmental conditions play a role in development, it would be incorrect to say that any structure or function which matures is purely inherited. Due to the major influence of heredity and genes upon maturation, birds start singing at a particular age, and children start walking and babbling at a particular age. Sexual growth also begins at a particular period of life, even though no training is given.
Hence maturation does not depend upon learning maturation can be accelerated by training, by the factors of the external environment. Maturation can take place without learning, within the four walls. A person can sit, stand, walk and babble without getting special training. A lot of research on maturation has been conducted on animals and some on human infants. Evidence of maturation is found in experiments on birds, rats, monkey,s and human infants.
Arnold Gesell (1946) conducted a study to examine the importance of maturation over learning. She took two twin girls, say A and B. At 46 weeks A was trained to climb stairs and she took several weeks to leam the skill. At 53 weeks B, her sister, was taught to climb the same stairs. She only took 2 weeks to leam it. This difference in learning can be well attributed to better maturation in the case of who was taught to climb stairs seven weeks after her sister A was taught.
The findings of this study make it clear that maturation helps one to leam much more quickly. It also suggests that maturation may not necessarily depend upon learning, but learning definitely depends upon maturation. Why? According to Boaz (1984) “for the learning of complex tasks, particularly for the symbolic learning, maturation of the cerebral cortex and its association areas is an absolute necessity.
Lashley’s experimental findings also show that learning ability directly depends upon the size of the cerebral cortex. That is why, when the child is not ready to leam, no amount of teaching or training will make any good. This is what everyone, including the parents and the teachers, should realize.
Kellog and Kellog (1933) conducted a classic experiment on “The Ape and the Child.” A human child Donald and a Chimpanzee baby Gua were brought up in the same environment and treated identically. Gua, who was two months younger than Donald was humanized earlier than Donald. Munn in this connection describes.
In learning to skip, cooperate with her foster parent, obey requests, kiss to makeup, open doors, anticipate her bowel and bladder needs, eat with a spoon, drink from a glass, and understand such expressions as “Kiss, Kiss” “Come here” Shake hands” and “Bad girl”. Gua was ahead of Donald. She learned faster than Donald because she was more mature.
The conclusions of this study are:
Though the Chimpanzee was of an inferior race and was superior to the child in certain respects due to greater early maturation, Donald could leam certain things like speaking, which Gua without special training could not leam, even though she was more mature. It is because men are more mature than apes.
![]()
Question 7.
Define (aw of learning). Describe the law of effect?
Answer:
On the basis of several experimental findings on animal learning. Thorndike formulated certain laws to explain the fundamental process of learning. Learning can be explained as an operation of these laws or principles.
Law of Effect:
It follows from the law of exercise. The Law of effect refers to some kind of reward or reinforcement. It stresses the role of motivation in learning. It is the consumer stone, the cardinal principle of Thorndike’s theory of learning. Thorndike viewed that in all situations involving learning. Law of effect in Thorndike’s opinion refers to the strengthening and weakening of connection as a result of its consequences.
When a modifiable connection is made and is followed by a satisfying state of affairs, the strength of the connection is increased. If a connection is made and is followed by an annoying state of affairs, the strength is decreased. If the hungry rat gets food after running the maze, it again runs the maze when hungry. But if it fails to get food, it will no more run.
Similarly, if the dog in the conditioned response method gets food, after salivating to bell it will again salivate to below. The learning which gives satisfaction is repeated over and over again. Conversely, failure and dissatisfaction will create an aversion to that learning. If several runs in a particular pathway do not lead to food, but to shock, the rat with a feeling of failure leaves that path and takes another, which leads to a reward.
If the animal is rewarded, next time it expects food and so learns quickly. Thorndike talks about the effect in operational terms. A connection is strengthened and associated with fulfillment of drive, weakened in the case of the opposite. The strength of connection takes place in terms of result i.e., it depends upon the result. The law of effect, therefore, can be called the law of consequence of results from this angle.
The satisfying consequences or results are retained and the dissatisfying ones are eliminated. Thorndike said, “By a satisfying state of affairs is meant one which the animal does nothing to avoid, often doing things which maintain or renew it. It is something that the animal always tried to maintain. An annoying state of affairs is meant one in which the animal does nothing to preserve often doing things that put an end to it.
Objections against the Law of Effect:
Some have argued that Thorndike’s reasoning is circular. Thorndike had to define satisfaction and annoyance in the manner of annoyance. In the pretension of defining a problem, he again comes back to the same problem. Another objection comes from Watson himself. He said that it has a subjective tinge. So he stated that satisfaction and annoyance are connected with some mental state and as such is inappropriate for the description of animal behavior.
Thirdly, the “backward effect” of the Law of Effect has been certified, because the effect going backward is not logical according to them. In Thorndike’s view learning consists of a series of S-R units like S -S2-S3-S4-S5 and so on. The effect comes only at 5. However, it not only influences S. but all the back stimuli like S, S, S3, and S4. But since learning is discreet, how can it be connected with other stimuli, and how the correct response at the 5th’ stage can again go back to the first one?
This idea of Thorndike is very legitimately doubted. To meet this criticism Thorndike argued that the effect of going backward is a matter of empirical observation and reality and hence should not be challenged. The Geslaltists rejected the law of effect. Their objections were based upon experiments and hence more troublesome for Thorndike, the Law of effect, in spite of this criticism is central not only to Thorndike but to all who believe in some sort of reinforcement in learning.
This was the position of Thorndike up to 1929. From 1929 onwards, a very great change took place in his theory, i.e., he modified it. The necessity of modification arose due to severe criticism from various contemporaries like behaviorists and Gestalt Psychologists. Thorndike was so much perturbed by the criticism coming from the Gestalt School and from Iris’s own experimental findings at the meeting of International Congress in Psychology (1927).
he confessed “I am wrong” With this statement, he suggested some radical modifications to his theory of trial and error. He completely gave up the law of exercise and so the law of effect after 1930 was called the “Truncated Law of Effect.” The weakening effect of punishment was also given up or renounced. Thus, he substituted only half of the original law of effect.
The other half dealing with punishment was given up as the negative side appeared to be unimportant for learning. He stated that mere occurrence was enough to counterbalance the eliminating force of punishment. This he did on the basis of his famous experiment on chicks. In a simple maze, the choice of three correct pathways was given such as:
- Freedom,
- Company,
- Food.
The wrong responses led to a punishment of confinement for 30 seconds. A careful record of the data was kept in regard to the times the chicks followed a path when it led to rewarding and it led to punishment. The aim was to examine if a particular pathway led to food or freedom or company or electric shock, and how often the different paths are repeated.
The findings of this study led Thorndike to conclude that rewarding a connection always strengthened it substantially, and punishing it weakened, it a little or not at all. Thorndike found that there was almost a universal view that reward was more efficacious than punishment. Contemporary psychologists called this the law reinforcement. Thorndike also discovered another important phenomenon in the law of effect.
It is known as The Spread of Effect. He noticed that the effect of reward was not only upon the connection with which the reward associated but also upon the neighborhood connections. Effect strengthens these connections which have preceded and followed reward. In short, reward not only strengthens the right connections but also the adjacent connections.
This Thomdike said is a kind of gradient effect. Subsequent experiments on the spread of the effect have yielded similar findings. Tiffin and Nuttin, for instance, got extensive results. However, this phenomenon of the spread of effect has been denied on experimental and statistical grounds. People said on the basis of empirical findings that the spread of effect is not real but conditional.
Thorndike’s theory after 1930 can be summarized as follows:
Reward is extremely urgent for learning. It minimizes the effect of punishment. In matters of potency, the reward is so potent counterbalances the effect of punishment. Rewarding connection always strengthens it substantially. Punishment weakens the connection little or not at all. Thorndike’s law of learning after 1930had a lot of social implications. The modification of this law is at the root of all social changes. It is more practical in classroom teaching, in jails, and in juvenile reform centers.
Spare the rod, spoil the child is based on this principle of learning. Canning has been banned in educational institutions. Physical punishment also is not in much use today. Thus, prisoners in jail, school students, and for juvenile delinquents laws of effect tremendous importance. The three important views about the law of effect are as follows Law of effect is essential to learning – Thorndike, Hull.
Question 8.
Discuss the few other laws of the theory of Thorndike and critical evaluation?
Answer:
Thorndike’s theory:
Thorndike has a number of subsidiary laws. They are The law of multiple responses, i.e. there are a number of responses at the disposal of the ‘O’. when one fails, one other is tried by the law of prepotency; and the law of associative setting. A few other laws of learning have also been referred to by Thorndike, which are discussed below:
Law of Contiguity:
Contiguity refers to nearness. Nearness can be two types, nearness of space and nearness of time. If two things are experienced together, either due to the nearness of space or time, when one is experienced, the other immediately comes to our mind. Blackboard and chalk, library and librarian are related by contiguity of space. When is face one, the other immediately comes focus of our consciousness? An example of the contiguity of time is thunder and lightning. When we see the lightning, immediately we anticipate the thunder which follows the lightning at once.
Law of Frequency:
It is a frequent occurrence that gives an advantage. When nerve connections are frequently used, they leave a particular mark on memory. This is suggested by Thorndike physiological change. It is very much related to the law of exercise. The Law of frequency and the law of exercise are sometimes considered as having equal functions.
Law of Recency:
Any act which has been performed recently has the advantage of being learned and remembered more quickly than the older, far-off, and distant experiences. The recent experiences are better remembered because Neural pathways involved in recent experiences are the last to be activated and the impression in the nerves is fresh. they were the acts nearer to the solution and satisfaction of the need.
The last attempt is the recent attempt and it is a nearer goal that gives a satisfying experience. So it is learned and remembered quickly. While learning the maze box, the rat remembers the last path move vividly as it brought food and satisfied its hunger need. Psychologists who have criticized the law of recency and the law of exercise believe that it is an atomic or molecular approach.
Law of Primacy:
First impressions last long. Other things being equal, all first-learned things are better remembered. The first time one meets a person, the first day of joining college, the first night of I marriage, and the first, time one joins a job or receives his pay packet are examples. Similarly, the first line of a song and the first syllable from a list of nonsense syllables are quickly learned.
Due to the operation of a law of primacy and recency, the first and last nonsense syllables of a list are more easily remembered than the materials in the middle of the list. The first things get enough time to be consolidated and there is no proactive inhibition in this case while in the middle series, both proactive inhibition and retroactive inhibition operate.
Law of Intensity:
If the experience is very intense and emotional, it is easily remembered and further learning may not be necessary to remember it. Certain childhood experiences which are extremely pleasant or deeply shocking like getting a gold medal as a reward, the sudden death of parents and failure in an examination may be remembered for the entire life because of their intense nature.
Intense experiences need not be repeated. One single experience will be enough to be remembered for one entire life. However, according to the theory of repression, if the experience is too shocking or unpleasant, it may be forgotten due to the operation of the mechanism of repression.
Law of Belongingness:
The Law of belongingness by its recognition of an organizing principle is foreign to the structure of Thorndike’s theory of specificity and mechanical action. Rather it gives some recognition to the Gestalt principles in learning. Attacked by Kohler, Koffka, and other Gestaltists for his neglect of organizational principles, Thorndike developed this law of belongingness. It states that the effect is stronger if it belongs to the stimulus-response connection.
Following this line, Thorndike said that if there is an S R connection and the effect belongs to it, the influence is weaker. When one is hungry, food belongs to the situation and so the hunger-food connection makes learning more efficient. When one is hungry, water does not belong to it, only food belongs to it, and only food can satisfy the need of hunger. The belongingness of reward and punishment depends upon the appropriateness of satisfying an arousal motive or want in the learner.
The concession to the principle of belongingness is a concession to the field psychologists who stress the field factor in every learning. Introducing this principle, Thorndike says that effect is more efficacious when it is an effect with belongingness. Belongingness of reward and punishment depends upon its appropriateness is satisfying.
An aroused motive or want in the learner and in its logical and informative relationship to the activities rewarded and punished. To be rewarded with a glass of water when one is thirsty is a reward with belongingness. Without belongingness, though the aftereffect cannot be denied, with belongingness they are more effective.
Critical Evaluation of Thorndike’s Theory:
Thorndike for the first time made a systematic and scientific study of the problems of learning. He developed methods of animal experimentation and gave such genetic and comparative psychology which provided the impetus for a tremendous amount of research on animal psychology. Looking at the theory of Thorndike, we find, it is one man who has created regular stomachs in the whole field of learning.
Though several decades have passed, still we find Thorndike at the root of all kinds of discussions in learning. Some of his ideas, though have been modified and improved, but the law of effect still continues to have a very significant place in learning. Chiefly two kinds of criticisms have been leveled against Thorndike. His stress on reaction performance, on parts rather than on whole has been criticized.
These are criticisms that result from differences in outlook and temperament. The second type of criticism is very fundamental and specific mainly against the law of effect. It was argued that the law of effect is subjective in nature and the backward nature of the law of effect was also criticized. There are also some important experimental criticisms like renunciations of punishment in the law of effect. While Mouren and others have viewed that punishment is very significant in the acquisition of behavior, taking the help of latent learning.
Tolman of the Gestalt School argued that learning can take place with simplicity without reward. The attacks by the Gestalt School in the 20s were more telling and Thorndike began to later meet some of these criticisms. But it was before the International Congress of Psychology Newttaven in September 1929, he came out with the statement “I am Wrong.”
Transfer of Training:
The theory of transfer of training refers to the popular concept that man should be given training in a general way which includes language, mathematics, and classics. They thought that training in these areas positively transferred to various walks of life. It was found that formal education is transferred to various life situations and vocations. The pattern of education at that time in England was, therefore, mainly restricted to classics, language, and mathematics.
Subsequently, there was a lot of discussion on the generalization of the transfer of training and transfer of mathematics to another subject. Thorndike was the first person to raise his voice against the unscientific character of this presupposition and said, it would be illusory to support that there is a transfer from mathematics to other subjects, He viewed that training in one subject helps the other subject only to the extent they have elements or aspects in common.
The identity may be in substance or in the procedure. Thus there can be a transfer from mathematics to statistics or knowledge of addition helps in multiplication; because both have necessary similarities. 11 hence, it is also called the “theory of identical elements”. Thorndike’s theory of transfer began to take shape in an experimental study done in collaboration with Woodworth (1903).
This study presupposes that transfer depends upon the presence of identical elements between the original and subsequent learning. What is implied by the transfer of training? When previous training or knowledge influences the acquisition of subsequent learning it is called a transfer of training. There are three types of transfer of training positive transfer, negative transfer, and zero transfer.
Positive Transfer:
In the positive transfer of training acquisition of skill in one situation facilitates the training in subsequent situations. For instance, knowledge of physics facilitates training in electronics. knowledge of mathematics accelerates the training in statistics or computer science; knowledge of language facilitates the study of classics and literature.
Positive transfer of training occurs due to the similarity of content, the similarity of technique, and the similarity of principle. Thorndike was of opinion that one activity influences another to the extent that they have common or identical elements. Contrary to the popular belief that transfer is general in nature, Thorndike put forth the idea that transfer is a matter of specific connections.
![]()
Question 9.
What is insightful learning? Discuss its characteristics and types?
Answer:
Insightful learning owes its existence to the Gestalt School of Psychology, particularly to its founders Kohler and Koffka. The theory of insightful learning developed as a revolt against Titchener’s structuralism, Thorndike’s trial and error learning, and part-whole relationship. As opposed to Thorndike, Gestalt developed and theory of whole part position in learning and perception.
Gestalt is a German word with no exact English translation. It more or less refers to the form organized whole and configuration. Objects and things are perceived and learned as a whole, in complete form. This is the salient point of the Gestalt School. According to Crow and Crow, Gestalt is a pattern a configuration of a form of apprehending a stimulus situation.
Characteristics of Insightful Learning:
Insightful learning, the ‘ O ’ reacts to the whole situation and not to some details only. The ‘ O ’ finds out the relationship between the various stimuli within the situation as a whole. The relationship that the ‘O’ perceives is mostly between a means and the end or goal. While learning by the insight the ‘ O’ modifies and restructures the perceptual field. A sudden change in the behavior of the ‘O’ is frequently observed.
The solution to the problem comes all of a sudden, in a sudden flash. The capacity for insightful learning is restricted by age and individual differences. Older children give a better response to learning by insight than younger ones. Similarly, higher animals like monkeys and chimpanzees solve problems by insight than guinea pigs. Insight depends upon past experience. However, the Gestaltists do not agree with this. They instead emphasize the present experiences of the learner.
But one must accept that a child cannot get into the heart of a mathematical problem unless the symbols stated therein are understood. For this, past knowledge of the subject is required. Even. when the problem is at the capacity level since he does not know the signs and symbols, he cannot solve the problem. Generally, it has been found that once one gets the idea for the solution to the problem in subsequent situations, that idea helps in solving the problem.
Insightful leaming needs experimental arrangement. The problem situation must be properly arranged and the tools must be kept systematically so that the necessary aspects are amendable to observation. If the required tool is out of the field of perception, solving the problem becomes difficult. Certain cases of insightful learning may be preceded by trial and error or a period for search or preparation.
In the stick and banana experiment, the first half was trial and error learning. Once achieved, insight can be used in a new situation. The same method can be repeated over and over again to solve new problems. The idea is thus transferred or carried over from previous to subsequent learning situations. In the case of human subjects, insight is often accompanied by verbal cues which help in subsequent learning. A solution of insightful learning can be readily repeated.
This has been proved in the case of the Sultan. When Sultan was again placed in the box with a bunch of bananas the next day, it repeated the same idea of joining the two sticks and getting the banana. Only it did not show any trial and error behavior as on the first day. In insightful learning we observe an integrating and reintegrating of part processes into a new total pattern, these part processes having been provided by experience, though the Gestalt School gives emphasis on the present situational factors.
Insightful learning can be of two types :
- Learning by Foresight.
- Learning by Hindsight Foresight
When the solution to the problem comes at once in the first attempt without actually trying the situation, it is called foresight. When a person solves a mathematical problem suddenly without using trial and method error it is a case of foresight. Hindsight Solution comes after trying with the elements.
Question 10.
Define observational learning?
Answer:
At the time there were rarely computer monitors in the airports of India showing the time of arrival and departure of planes indicated by their flight numbers. Only there were occasional announcements. I was waiting for a security check-up along with so many other passengers who were waiting for different flights with boarding cards of different colors kept in their shirt (front) pockets. I was a little nervous and worried because I was not very sure if I could be able to go to the right gate for a security check-up and board the right plane.
My boarding card was pink in color. Immediately I got the intrusion to follow the passengers who had also pink-colored boarding cards. I observed them and found four, or five passengers with pink colored cards, and I gave a sigh of relief. When there was a call for a security check-up, occupants of the pink-colored card got up to proceed and I quietly followed them and arrived at the right gate for the security check-up.
Subsequently, things became easy for me. I observed and imitated the activities of my co-passengers and followed them till I reached the plane. When the plane was about to take off, the air hostess announced that every one should fasten their seat belts. I tried with the seat belt but could not fasten it around my waist. Then I observed my co-passenger silently and learned the technique.
These are examples of observational learning. Observational learnings are most common in our day-to-day life. Observational learning in most cases is a simple type of learning whereby watching others in activities we learn a lot. Even we leam abstract rules, concepts, and ideas by observing others’ behavior either in reality or from cinema or T.V. Thus while watching T.V. people also learn to do things.
People leam social customs, rules, regulations, traditions, rituals, and cultural heritages of the society by observing others so that many embarrassments are avoided. When a child sees his mother showing respect to another person, the child also does the same. The child also does the same. ‘In society we leam from other people’s experiences by observing them, watching them. In fact, people leam both positive and negative behavior patterns like sociability and aggressiveness through observation of models.
Bandura, the pioneer of observational learning opines that it is a third major way by which we leam next to trial and error and conditioning. Several research findings suggest that observational learning places some role in every aspect of human behavior and we cannot manage without this method of learning. We leam cooking, stitching, washing clothes, toilet habits, knitting, making art and drawings, decorations by watching other people doing the same.
Even we leam a lot of necessities of day-to-day life by watching the T.V. Most of the household activities and various exercises are learned through observation. Many experiments on children prove this point. The famous Bobo doll experiment of Bandura, Ross, and Ross (1963) indicate how children leam to be aggressive by observing an adult aggressive model. They took two groups of nursery school children as samples. The control group was exposed to a non-aggressive amiable adult model.
But the experimental group was exposed to an aggressive adult model who kicked a big doll, scolded and insulted it. Then the children of both groups were allowed to play in a room with several toys. Children of the experimental group showed more aggressive behavior towards their toys and dolls compared to the children of the control group. This may also be called “Imitation Learning”.
Social scientists explain the indisciplined, aggressive, unruly violent, and ruthless behavior of many modem youths as a consequence of imitating the same from T.V. Cinema and video films. The ability to learn by observing others’ activities is due to the cognitive influence of learning. Even Toman’s experiment on rats learning to run mazes substantiates the fact that simple creatures can learn from experience to form internal models to guide later behavior.
Basic Principle of Observational:
The principles of observational learning explain what factors and conditions determine whether and to what extent we learn information skills, concepts, and ideas from others’ behaviors. Following are four basic principles of observational learning as suggested by Bandura.
The direction of attention to appropriate models performing a particular activity:
People generally imitate such people’s behavior which seems appropriate to serve their purpose or aim. Intelligent, pretty, attractive people demonstrating cognitive ability, having unique status, and success come under this category.
Remembering the actions, behaviors and skills shown by the model:
In order to be successful in observational learning, the person must retain what he has observed from his model so that he can behave in a similar way when required.
Production process or conversion of the retained behavior of the model into appropriate action at the time of requirement:
According to Bandura production processes depend upon one’s own physical abilities which can give a clear representation of its memory at the appropriate time, and the capability to monitor one’s own performance and manipulate it till it matches the behavior of the model.
Motivation:
In Bandura’s view, one may observe another person’s behavior but he may not convert it to action unless he is motivated to do so. Only those behavior that is required and useful for a person, he is motivated to practice them, so motivation is required to observe actively other’s activities and put them into practice.
Observational learning may not always be as simple as it appears. It is more complex than mere learning by imitation. It plays an important role in modifying our behaviors through observation. Observational learning leads to aggressive behavior (Baron and Richardson, 1994, Central wails 989, Synder, 1991, Wood, Wrong, and Chachese (1997). Children are found to show aggressive behavior after imitating their age mates.
It can also be used as a technique to train workers for the improvement of interpersonal relationships. Sociability, courteousness, and amiability can be developed by observing these qualities regularly in other people. Culture shock can also be avoided through observational learning. Asian and Western cultures differ contrastingly. It becomes difficult for people of both cultures to adjust and interact normally with each other. Similarly, with the globalization of the world economy, people of different cultures have to interact with each other when they meet.
![]()
Question 11.
Define the stage of insightful learning. Differentiate between insightful learning and trial, and error learing?
Answer:
Stages of insightful learning:
Need:
Like any learning, the need to leam is essential in insightful learning. The need may be biological like hunger, sex, or thirst or social like gregariousness, or personal like the desire for power, prestige, and recognition.
Preparation:
Preparation is a basic precondition before insightful learning starts. In Kohler’s experiment on the Sultan with problems involving the use of readymade implements, there were preliminary preparations for the learning. The leader makes various surveys, inspections, and acute examinations of the problem and its field.
Incubation:
It refers to the stage of clearness or dormant period when all overt activities are suspended. It is a period of progress when the ‘O’ silently thinks over the problem.
Inspiration:
In this stage, the idea for the solution to the problem comes suddenly. It flashes in the mind at once. The bright ideal, the “brain wave” comes to the mind during this stage. This stage is sometimes characterized by shouting and jumping in joy, as the ‘O’ is enlightened by the bright idea which came in a flash.
Verification:
It is the last stage of insightful learning in which the ‘O’ makes practical application of his bright new idea. In the case of the Sultan, it joined both the sticks, placed the boxes one after another, and got upon the third box, and brought the bunch of bananas hanging on the roof.
Critical Analysis of Insightful Learning Theory:
Kohler, Koffka, and other advocates of insightful learning have stated that perception of the relationship between different parts of the visual field and the goal plays a significant part in learning. They have also said that learning by insight takes a single attempt to solve a problem. But this is not the fact in reality. In most cases, we find that learning is a gradual process and the errors reduce gradually which the insight theory is not ready to accept.
So insight is not the only method of learning. It is nevertheless one of the methods of learning. Practice is also essential for learning. But practice is totally unacceptable to Gestalt psychologists. However, it can be said that in every difficult and complicated situation the only type of learning that is involved is insightful learning. Munn (1953) thus comments, “Insight is rare in animals, not quite so rare in children and quite common in human adults!”.
While American psychologists have mostly used mazes and puzzle boxes, German psychologists, used situations where all relevant aspects of the problem are visible. Thus Bertrand Russel remarked “Animals studied by Americans run about frantically, with an incredible display of hustle and pep, and at last achieve the desired result by chance. Animals observed by Germans still and think and at last evolve the solution out of their inner consciousness.”
Difference between Insightful and Trial and Error Learning:
Trial and error are more often found in lower animals and children while insightful learning is rare in animals, not so rare in children, and commonly found in human adults. Trial and error learning depends upon practice and repetition while insightful learning does not require much practice. Trial and error learning is mechanical, random, blind, a hit-and-miss type of learning where a solution comes by chance, accidentally.
Insightful learning depends upon intelligence, understanding, grasping, and perception of the whole field of the organization. Trial and error is a simple type of learning mostly found in the acquisition of skills, particularly motor skills. Insight is a complex method of learning. It is more effective in cognitive and verbal learning. Trial and error learning is gradual and slow. Several trials are required to lead.
Insightful learning is sudden and comes abruptly at once in a flash. One trial is necessary for learning. Trial and error learning is more or less temporary. When practice is given up, the acquisition of skill fades up. Insightful learning is permanent as it grows out of understanding the relationship between the tools and the goals. In trial-error learning, a reaction to a part and specific stimulus is made.
In insightful learning, the situation is perceived as a whole to bring the solution. Trial and error learning does not involve insight. Learning by the insight in many cases involves some amount of trial and error. Trial and error depend upon practice and past experience. Gestalt School argues that it does not depend upon past experience which is a controversial view. Learning is transferred from one situation to another on the basis of transposition. In insightful learning transfer of training takes place in the form of identical elements,
Question 12.
What is classical conditioning? Describe determinants and basic processes in classical conditioning?
Answer:
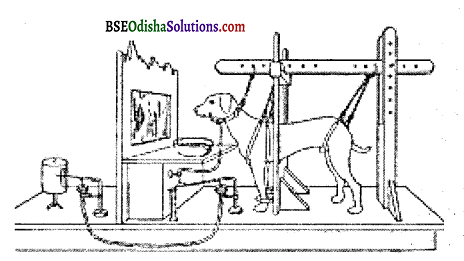
This type of learning was first investigated by Ivan R Parlov (1849 -1936). He was an eminent Russain Psychologist and a Nobel prize winner for his work on the physiology of digestion. During his studies, he observed that dogs started secreting saliva as soon as they did. Sighted the empty plate in which food was served. As we are aware, saliva secretion i.e. reflexive response to food or something in the mouth.
This observation led to the famous conditioned response of learning. Pavlov designed an experiment to understand this process in detail. In the first phase, a dog was left in a box and harnessed. The dog was left in the box for some time. This was repeated a number of times on different days. Then a simple surgery was made and one end of the tube was inserted in the dog’s jaw and the other end of the tube was put in a measuring glass.
Then, in the second phase of the experiment, the dog was deprived of food and was kept hungry. Again, the dog was placed in a harness with one end of the tube in the jaw and the other end of the glass jar. Now a bell was sounded and then meat powder (food) was served. The dog was allowed to eat it. This exercise was repeated for a few days. After a number of trials, a test trial was introduced in which the set up was the same except for the presentation of food.
In the first phase, the dog was secreting saliva in response to the Unconditioned Stimuli (US). But after conditioning, salivation started to occur in the presence of the sound of the bell (CS). Here, the bell becomes a Conditioned Stimulus (CS) and saliva secretion, a Conditioned Response (CR). Here, it is obvious that the learning situation in classical conditioning is one of the S-S learning, in which one stimulus (i.e. bell sound) becomes a signal of another stimulus (i.e. food).
So one stimulus signifies the possible occurrence of another stimulus. Examples of classical conditioning are many. Suppose someone has finished lunch and was satisfied with his food. But suddenly he saw some sweet dish served on the adjoining table. Then the secretion of saliva in his mouth became automatic. He felt like eating it. This is a conditioned response (CR).
| Stages of Condition | big Operations |
| (a) Before | Sound of Bell -Alertness (No specific response) |
| (b) During | Sound of the Bell (CS) + Food (US) – Salivation (UCR) |
| (c) After | Sound of the Bell – Salivation (CS) (CR) |
Determinants of Classical Conditioning:
Practically, the acquisition of a response occurs very quickly and strongly in classical conditioning. But how it occurs depends upon several factors. Some of the major factors influencing learning a CR are enumerated below.
Time relations between Stimuli:
Basically, there are four types of classical conditioning procedures. These procedures are based on the time relations between the onset of conditioned (CS) and, unconditioned stimuli (US). The first three are called ‘Forward Conditioning’ procedures and the fourth one is called the ‘Backward conditioning’ procedure.
The basic experimental arrangements of these procedures are as follows When the onset of CS and US are concurrent, it is called simultaneous conditioning. In delayed conditioning, the onset of CS precedes the onset of the US. The CS ends before the end of the US. In trace conditioning, the onset and end of the CS precede the onset of the US with some blank time between the two.
In backward conditioning, the US precedes the onset of CS. Now it is obvious that the delayed conditioning procedure is the most directive way of acquiring a CR. Again, simultaneous and trace conditioning procedures require a greater number of acquisition trials in comparison to the delayed conditioning procedure. But the acquisition of response under a backward conditioning procedure is very rare.
Type of Unconditioned Stimuli:
I.P. Pavlov used two types of unconditioned stimuli in classical conditioning – appetitive and aversive. Appetitive unconditioned stimuli automatically elicit approach responses, such as eating, drinking, caressing, etc. But the aversive US is painful, and harmful and elicits avoidance and escape responses. Examples are noise, bitter taste, electric shock, painful injecting, etc.
The observation indicated that appetitive classical conditioning is slower and requires a greater number of acquisition trials. But depending on the intensity of the aversive US, aversive classical conditioning can be established in one or two trials.
The intensity of Conditioned Stimuli:
The intensity of CS influences the course of both appetitive and aversive classical conditioning. It observed that more intense conditioned stimuli are more effective in accelerating the acquisition of conditioned responses. In other words, the more intense the CS, the fewer the number of acquisition trials required for conditioning.
Basic Process in Classical Conditioning Parlov’s classical conditioning is an extremely simple form of learning. Truly speaking, it is regarded as the building block of all forms of learning from simple to more complex. The basic processes involved in Pavlovian conditioning are enumerated below.
Acquisition:
In the classical conditioning experiment, the paired presentation of CS and UCS is called a trial. The period in which the organism learns the association between the CS and UCS is the acquisition phase. As the trials continue, the CS becomes gradually stronger to elicit the CR. Presenting UCS with CS during the acquisition phase is a critical operation in classical conditioning.
Here the UCS serves as a reinforcer because it reinforces the connection. Again, the trials on which UCS occurs are called reinforced trials and the trials on which the UCS is omitted are called unreinforced trials. At the beginning trials of the acquisition phase, the strength of CR increases rapidly.
The rate of acquisition during the reinforced trials depends on several factors. The important factors are the time – interval between the CS and the UCS. the intensity of the CS. the intensity of the UCS and the reliability of the CS in predicting the onset of UCS. As the reinforced trials continue, the strength of CR increases but not as rapidly as it used to be in the beginning trials.
Extinction:
When the CS is repeated without UCS then the CR gradually weakens and finally disappears. The disappearance of the CR due to non reinforcement is called extinction or experimental extinction. In the classical conditioning experiments, if a bell is presented time and again without food (reinforcement).
the amount of salivation gradually decreases and finally disappears. In short, when the reinforcement is withdrawn, the CR fails to appear. But extinction is not forgetting. The CR is only temporarily suppressed and after a brief rest period, a part of CR appears.
Spontaneous Recovery:
According to Pavlov, complete or permanent extinction of conditioned response is not possible. The reappearance of an extinguished CR after a Rest period is known as spontaneous recovery. Here the CR is partially recovered after a Rest period. hr classical conditioning experiment, after the salivation response, was given a rest period for thirty minutes.
After this span of rest, the bell was presented without food (UCS), following it. Then the salivation to bell suddenly reappeared. Very often, the response is successively extinguished when it reappears, then the spontaneous recovery diminishes. As a result, the CR fails to be shown even following the rest period. This is known as permanent extinction.
Stimulus Generalization:
In conditioning, generalization occurs to a certain class of stimuli rather than to a specific stimulus. In short, it is a tendency for the CR to be aroused by a similar stimulus.

In Pavlovian conditioning, the dog was conditioned to salivate to a specific tone. Then the CR is generalized to a second tone similar in characteristics to the first tone. As a result, a new procedure began. The first tone (CS) and the second tone (new stimulus) were presented on alternate trials. The first tone was followed by food (reinforcement) and the second was never followed by food (no reinforcement).
Consequently, the CR to the first tone was maintained and the generalized response to the second tone invited extinction. The dog learned to salivate to the first tone and to withhold salivate to the second tone. Finally, the dog was able to discriminate between the two stimuli because of differential reinforcement.
Like generalization, discrimination has also an adaptive significance, too much generalization is over-responsive, whereas, too much discrimination is over-selective. In a sophisticated manner, conditioning is a process in which discrimination ultimately wins over-generalization. Salivation to light by frequently associating it will bell but without presenting the food is called second-order conditioning.
![]()
Question 13.
Define operant conditioning?
Answer:
There are two main forms of simple learning. One is Classical and the other is Instrumental, Instrumental conditioning is also known as operant Conditioning. You can take a simple example here to describe instrumental behavior. When a dog responds to the commands of its master to get some biscuits, the dog has learned an instrumental response. The dog is rewarded for a particular response.
In nutshell, the dog’s response was instrumental in fetching a sought-after reward. That is why it is called instrumental conditioning. This type of conditioning was first investigated by B.F. Skinner. He studied conditioning of voluntary responses found when an organism operates on the environment. He called them operants. Operants are that behavior or responses, which are emitted by animals and human beings voluntarily and are under their control.
Here the very term ‘Operant’ is used because any organism operates on the environment. Skinner conducted His experiments on rats and pigeons in specially designed boxes, known as Skinner boxes. A skinner box usually contains a mechanism for delivering a consequence whenever the animal in the box makes a readily identifiable response that the experimenter has decided to reinforce or punish.
In experiments that involve rewards, the delivery mechanism is often a small lever or bar on the side of the box. Whenever the animal inside presses it, the response is rewarded (B.F. Skinner, 1938,1956). In his experiment, Skinner put a hungry rat in the chamber, which was so built that the rat could move inside but could not come out. In the chamber, there was a lever, which was connected to a good container kept on the plate placed close to the lever.
The hungry rat accidentally pressed the lever while moving around and pawing the walls (exploratory behavior). The hungry rat ate the food and in the next trial, after a while, the exploratory behavior again starts. As the trials increase, the rat takes lesser and lesser time to press the lever for food. However, conditioning is complete when the rat pressed the lever immediately after it is placed in the chamber.
It is obvious that lever pressing is an operant response and getting food is its consequence. In this situation, the response is instrumental in getting the food. That is why this type of learning is also called instrumental conditioning. Examples of instrumental conditioning are around in our everyday life. Flumen beings leam shortcuts to attain desired goals through instrumental conditioning. Through this process, children learn to be polite and say please to get favors from their parents and others.
Here the response is changed according to the need and the demand of the individual. The response is made and determined by the organism himself. This is the most distinguishing feature of operant behavior. The organism is capable of making varied types of responses according to the demand of the environment.
Recently biofeedback technique is being used in instrumental conditioning which informs the individual about his unknown physiological function. But if is still unknown whether biofeedback provides direct control over involuntary responses or whether this control is mediated by voluntary processes.
Determinants of Operant Conditioning:
No doubt, operant or instrumental conditioning is a form of learning in which behavior is learned, maintained, or changed through its consequences. Such consequences are known as reinforcers. A reinforcer is defined as any stimulus or event, which increases the probability of the occurrence of a (desired) response. In other words, the stimulus event which increases the probability that behavior will reoccur is called a reinforcer (Or reward).
The impact or consequence generated by a reinforcer is called reinforcement. By contrast, a publisher is a stimulus event that decreases the probability that the behavior will reoccur. The impact of punisher punishment. Punishment is more likely to be confused with negative refreshment since both involve an aversive stimulus that the individual likes to avoid or escape from Always remember that the negative refreshment increases the response probability whereas punishment decreases the response probability.
On the whole, positive and negative reinforcements are procedures that increase or strengthen behaviors. An organism obtains reinforcement in two ways by obtaining a pleasant stimulus and by avoiding a painful stimulus. There are two types of reinforcement – Positive and Negative. In positive reinforcement, the probability of a response increases, because it is followed by a pleasant stimulus. In negative reinforcement, the response probability also increases, because the response removes an unpleasant stimulus.
Schedules of Reinforcement:
The reinforcement schedule refers to the arrangement delivery of reinforcement during conditioning trials. Each schedule reinforcement influences the course of conditioning in its own way. In our life instances, reinforcement comes on and goes off unpredictably. In many instances, reinforcements are delivered according to rules. For example, we receive a salary every month according to the rules. When the reinforcement is continuous, every occurrence of behavior is reinforced.
This simplest form of reinforcement delivery is termed a “continuous reinforcement schedule If the pigeon receives a food pellet every time it presses the tire lever, it is on a continuous reinforcement schedule. The other type is partial reinforcement (intermittent reinforcement). In partial reinforcement, the response is not rewarded every time it occurs. This type of reinforcement is conducive to maintaining learned behaviors. Once a response is learned under this schedule, it takes a longer span of time to be extinguished.
Four types of partial reinforcement schedules are:
- Fixed-interval
- Variable-interval
- Fixed ratio and
- Variable-ratio.
In the fixed-interval schedule, the organism is rewarded for the first response occurring after a fixed interval of time. Students increase their study hours as the examination approaches. The pigeon is rewarded for the first lever-pressing response occurring after one minute interval.
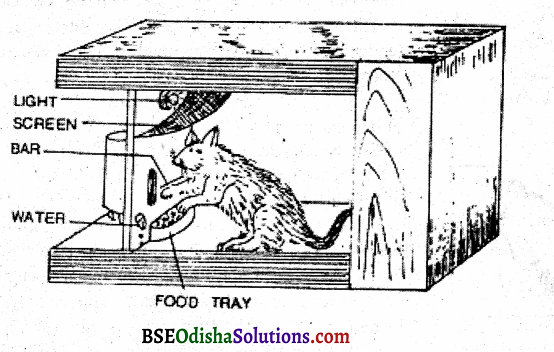
In a variable-interval schedule, the organism is rewarded after a variable amount of time has elapsed. The hungry rat gets the food pallet after 2 minutes, the next one after 5 minutes, the third one after 3 minutes, and so on. 1 Here, the organism responds at a steady rate in the variable interval schedule as reinforcement may come any time. Gambling behavior is the best example here.
| Schedules of Partial Reinforcement | Time Interval (Interval) | No. of Responses(Ratio) |
| Predictable | Fixed-Interval (low response) rate after each reinforcement | Fixed-Ratio (high) response rate with brief pauses after each reinforcement |
| Unpredictable (Variable) | Variable-Interval Steady response rate | Variable-Ratio (high and steady response rate) |
![]()
Question 14.
What is cognitive learning? Describe insightful learning and its stages or features?
Answer:
The process of acquiring knowledge about the environment which has an internal mental representation is called cognition. But learning is a relatively permanent change in behavioral tendency. The two terms are put together to generate the term ‘cognitive learning.
Two forms of cognitive learning:
- Insightful learning.
- Observational learning.
We first discussed the:
Insightful Learning:
I. P. Pavlov, S.L. thorndike and B.F. Skinner was all behaviorist. Obviously, they have ignored the study of learning based on reason and intelligence thinks when it learns. The chimpanzee evaluates the information in the learning situation and learns to reach a goal by developing insight. Wolfgang Kohler (1887-1968) arrived at Tenerife, the small island of the West Coast of Africa, to take charge of an institute for the study of the anthropoid apes, he was a German psychologist.
He was forced to stay on the island during World War-I. He engaged himself in an intensive study of how chimpanzees perceive, think, and learn. The results were translated into English in 1925 with the little ‘The Mentality of Apes’. Kohler used five types of problems to study how Chimpanzees solve complex problems. The two most fascinating and important problems were the ‘stick’ problem and the ‘box’ problem. Both these problems involved insightful solutions.
Besides chimpanzees, he also used dogs, hens, and little girls as subjects in his experiments. Kohler placed a hungry chimpanzee named Sultan inside a cage in the ‘stick problem. A bunch of bananas was kept outside the cage beyond the direct reach of the Chimpanzee. Two hollow bamboo sticks were kept inside the cage. One of them is very short and the other one is long. Since the sticks were hollow, one stick could be pushed into one end of the other to form a longer stick.
The bananas were kept at such a distance that neither of these sticks alone would be sufficiently long enough to reach the banana. But the Chimpanzee could get the banana if the two sticks were joined. The goal of the Sultan was to fetch the banana since he was hungry. Initially, he has shown all types of reactions that, generally, a Chimpanzee shows inside a cage. First, he used one of the sticks to draw the banana towards him but did not succeed. Then he tried the other sticks but in vain.
After some unsuccessful attempts, Sultan gave up the idea of getting food and sat in one corner of the cage. Then, after a short span of rest, he started playing with the sticks. He pushed one stick out as far as it could go and then pushed the first stick with the other until the first touched the banana. He started playing with the sticks again and accidentally one of the sticks went into the hollow end of the other. A sudden insight dawned upon Sultan and he solved the problem mentally.
Then he used two sticks to form longer sticks and with the help of this long stick, he pulled the banana inside the cage. When he faced the same problem on the next day, he solved it immediately. In another situation, Kohler demonstrated insightful learning in the ‘box’ problem. Here a bunch of bananas was kept on the tire ceiling of a cage, which Sultan could not reach. There were some empty boxes inside the cage. After some trials and errors, the animal could be able to snatch bananas by stacking several boxes.
Stages of Insightful Learning:
Here, the organism needs to reach a goal by solving a problem. The subject (learner) makes inspections, surveys, and examinations of the problem and the stimulus field. The ‘incubation period’ begins after an initial period of trial and error, all overt activities are withdrawn at this stage. The organism sits silently and thinks over the problem. Suddenly the organism develops insight into the problem after the incubation period.
The subject (learner) makes an attempt to make practical verification of his idea or insight about the problem. Once the subject achieves insight and solves the problem, the organism repeats the same method of solution without any hesitation. The organism attends to the relevant aspects and ignores the irrelevant ones when it attempts to solve similar problems in the future.
Common features of Insightful Learning:
Very often, the question arises – what does Kohler mean by ‘insight’ According to him, the common features of insightful learning are as follows The experimental situation is very important in insightful learning. The organism must be able to perceive the relationship among all relevant parts of the problem before insight can occur.
In this type of learning, the organism reacts to the whole situation, not to its component parts. Perceiving the relationship between the means and goal is very important in insightful learning. He also restructures the perceptual field during experimentation. Insight is followed by a period of trial and error behavior. During this span, the organism does not exhibit blind and random attacks as shown by Thomndike’s cat.
On the contrary, he tests behavioral hypotheses in the form of accepting some and rejecting others. The insight solution comes all of a sudden. Once the insight is reached, the organism shows a high degree of retention and transfer to similar problems. There is a correlation between insight and the capacity of the organism. This capacity depends upon age, experience, and individual differences.
Must Read: